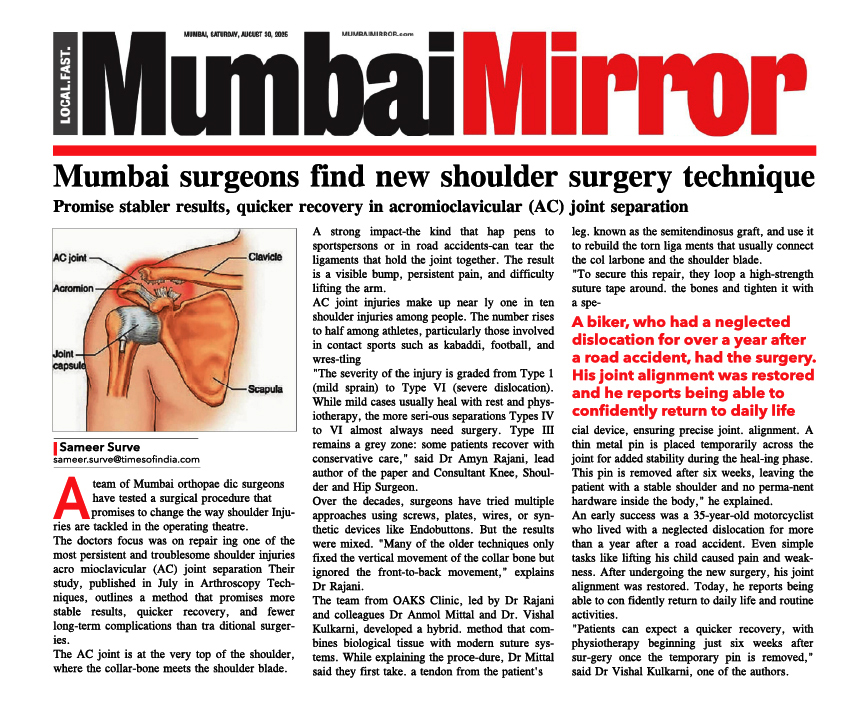
Fractures After Total Knee Replacement
Introduction:
Fracture occurring around a Knee which has undergone Total Knee Replacement are called Periprosthetic Fractures. Although not very commonly seen, Fractures in a prosthetic Knee have been reported in international literature. Fractures of Femur, Tibia and Patella can all occur following injury to the prosthetically replaced Knee.
Periprosthetic Fractures involving Femur
Risk Factors:
- Femoral notching done during the Total Knee Replacement
- Osteoporosis
- Osteonecrosis of Femur
Investigations:
X-rays:
Anterior-Posterior views, lateral views and oblique views are all required.
Conservative Management:
Non-operative treatment is avoided, except in patients with excessive comorbidity. This may include traction or plaster cast.
Surgical Management:
The Fractures can be fixed by retrograde nailing of the Femur Fracture or by fixation with a plate and screws.
Periprosthetic Fractures involving the Tibia
These Fractures usually involve the Medial or Lateral Condyle of the Tibia.
Risk Factor:
Osteoporosis
Investigations:
X-rays: Anterior Posterior Views and Lateral Views
Conservative Management:
- No role of Conservative Management
Surgical Management:
- Removal of the original Tibia tray.
- Fixing a Fracture with screws and using bone graft if required.
- If the fragment cannot be fixed then a step cut is done for the Tibia and the step is replaced by metal wedge on the Tibial tray.
Periprosthetic Fracture involving the Patella
Risk Factors:
- Not leaving adequate Patella after shaving (Patella left behind is less than 12mm)
- Use of central pegged implant
- Devascularization of Patella after a lateral retinacular release
- Excessively thick Patella
- Component malalignment
Investigations:
Lateral X-rays:
Fracture may be missed if undisplaced
Bone Scan:
If strongly suspected Fracture due to anterior Knee Pain and not visible on X-ray.
Conservative Management: Indicated in the following
- Intact extensor mechanism
- Patellar component is in place
- No comminution
- Displacement is < 2 cm
Conservative management involves immobilization in a plaster cast from groin to ankle for a period of 6 weeks, after which Knee is mobilized with the help of continuous passive movement machine.
Surgical Management:
This involves partial or complete Patellectomy depending upon whether the component is in place.
Partial Patellectomy: If component is in place.
Complete Patellectomy : If component is loose.