The following knee strengthening exercises are designed to recover strength of the muscles of the knee. You should talk over the suitability of these exercises with your orthopaedic surgeon or physiotherapist prior to start them. Usually, they should only be done provided they do not cause or rise pain.
Knee Exercises are divided into three types: Simple, Intermediate and advanced depending on the different knee pain reasons
Knee Strengthening: Basic Exercises
To initiate with, the following basic knee strengthening exercises should be done approximately 15 times, 3 to 4 times daily. As your knee power improves, the exercises can be advanced by progressively increasing the repetitions and power of contraction provided they do not cause or increase pain.
Quads over Fulcrum
Initiate this exercise lying on your back with the help of a rolled towel or foam roll under your knee and your knee should be in relaxed position. Gradually straighten your knee as far as possible tightening the front of your thigh also called as quadriceps. Hold for 5 to 10 seconds and repeat 10 times as hard as possible hurt free.
Static Inner Quadriceps Contraction
In this exercise you need to tighten the muscle at the front of your thigh also known as quadriceps by pushing your knee down into a folded towel. No you can place your fingers on your inner quadriceps (VMO – vastus medialis obliquus) to feel the muscle stiffen during contraction. Hold for 5 to 10 seconds and repeat 10 times as hard as possible hurt free.
Static Hamstring Contraction
Start this exercise in sitting with your knee bent to approximately 45 degrees. Press your heel into the ground tightening the back of your thigh that is; hamstrings. Hold for 5 to 10 seconds and repeat 10 times as hard as possible hurt free.
Here we will discuss different stage of Knee exercises for knee pain treatment
These exercises are frequently done as soon as possible after damage only if pain will permit. The aim is to reestablish range of motion devoid of putting any damaged tissues under pressure and solve your knee join pain problem. The precise exercises and how quickly you develop will depend on the type and harshness of injury. Active flexibility exercises where the athlete bodily attempts to move the joint through a range of movement are often the first step.
Early stage knee training’s
These exercises are done as soon as pain agrees. In some cases early stage of knee training can be performed within a day after the injury which starts after the acute stage.
Mid stage knee exercises
During the mid-stage, exercises progress to gentle Strengthening, slowly increasing the load on the joint and through the improving tissues. Balance and proprioception training generally begins.
Advanced knee exercises
Later stage or advanced knee exercises are more useful and sports specific. The aim is to repair full strength and flexibility to the joint and return the athlete to full training and race.
General post-surgical guidelines
Weeks 1 – 2
- Dressing change and review of home program.
- Ice/elevation every 2 hours for 15 minute to minimize edema and promote healing (please refer to Icing – Recommendations handout).
- Avoid impact or twisting for 4 weeks.
Manual
- Soft tissue treatment to quads, posterior musculature, suprapatellar pouch, popliteal fossa, iliotibial band and Hoffa’s fat pad.
- Patellar mobilization as needed.
- No direct scar mobilization (Avoid direct palpation and mobilization on incisions/portals for 4 weeks).
Exercises
- Strength training specifics: quad sets/straight leg raises, hip abduction, calf presses/heel raises, Gluteus sets, and core conditioning.
- Upper body conditioning, well-leg stationary cycling or Upper Body Ergometer (arm bike).
Gait training progression towards minimizing assistive devices (walker, crutches, etc).



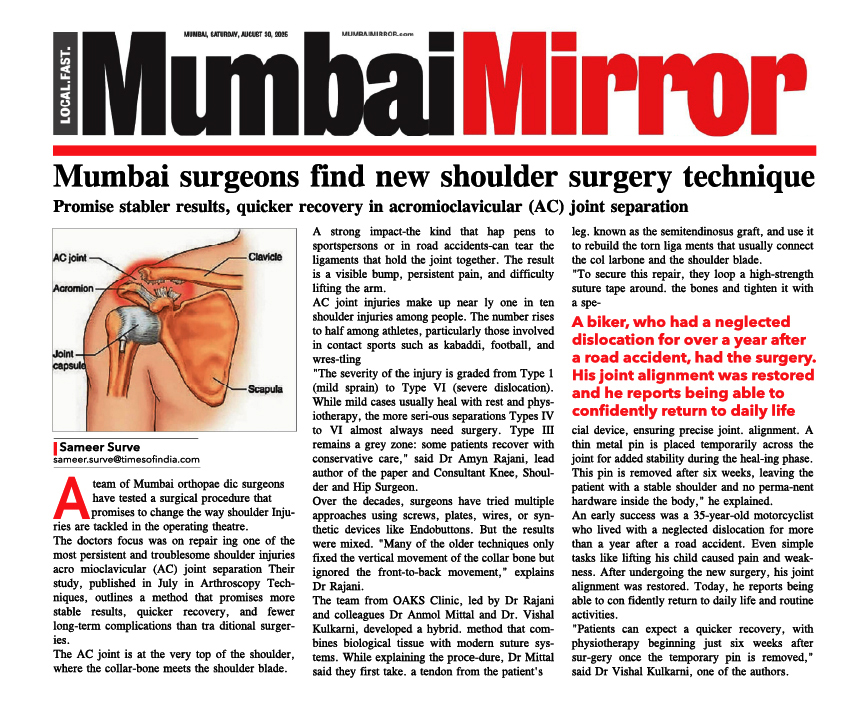
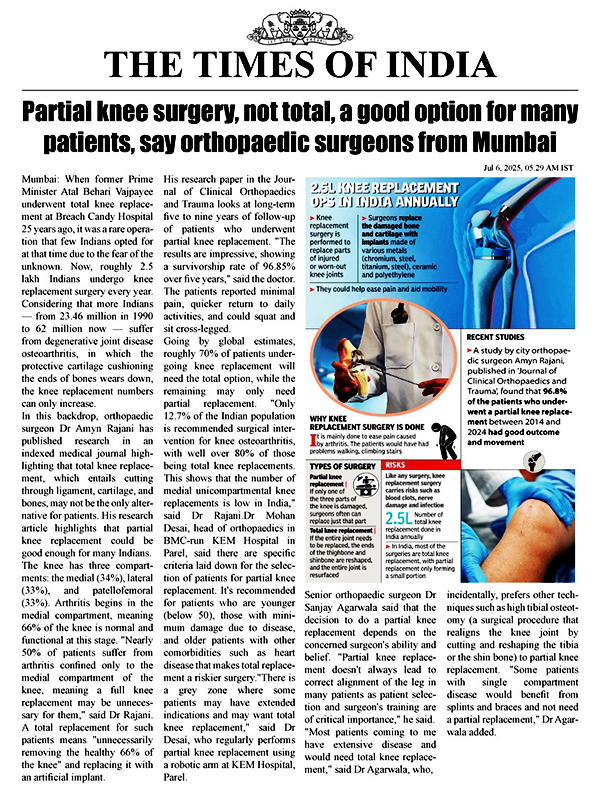
People of all ages experience knee joint pain, which has a variety of causes, including overuse, arthritis, and injury.
Knee joint pain may be experienced by in anyone and at any age. As we grow older, we might experience joint pains due to tissue degeneration.